Summary of the Article
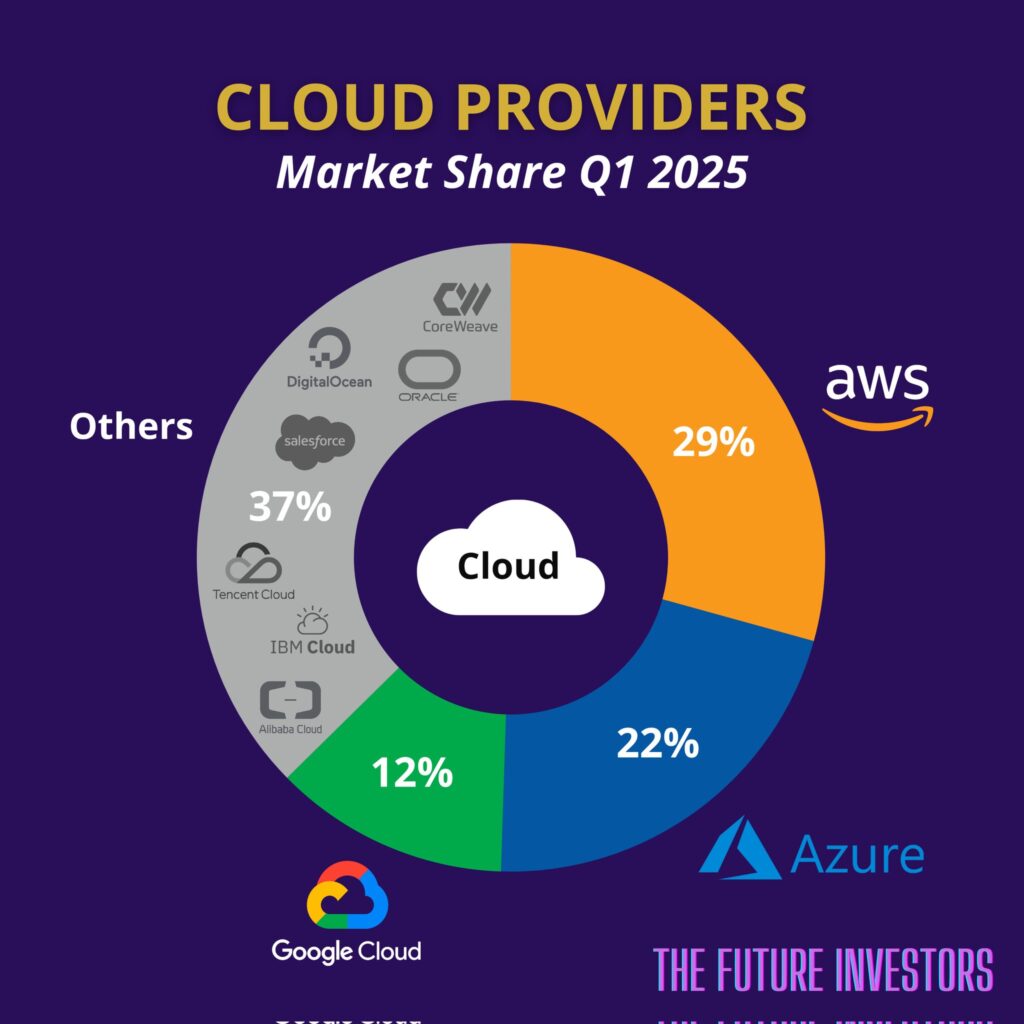
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) continues to dominate the cloud market with a 30% share in Q2 2025. Microsoft Azure follows with 20%, and Google Cloud takes the third spot with 13%. Combined, these three giants control 63% of the global cloud infrastructure market.
- The global cloud services market hit $99 billion in Q2 2025. Approximately half of this growth is driven by generative AI technologies.
- Google Cloud set a new record with a 13% market share in Q2 2025. This is the highest growth among the major providers, with a 1% increase from previous quarters.
- Even with strong competition, AWS has managed to maintain a market share of between 29-33% over the past several years. This shows impressive stability at the top.
- As the market continues to evolve with AI integration and specialized service offerings, cloud infrastructure decisions are becoming more strategic for enterprises.
Cloud infrastructure remains the foundation of digital transformation in 2025. While market leaders are solidifying their positions, competition is heating up. The latest market analysis reveals changing dynamics as enterprises are increasingly moving mission-critical workloads and deploying next-generation AI applications to the cloud. The latest industry report provides a detailed view of how the market is changing in this critical year for digital infrastructure.
The cloud infrastructure market worldwide is still under the control of a few tech giants, with the top three providers controlling almost two-thirds of the global expenditure. This concentration of market power hasn’t stifled innovation. Instead, it has increased the speed of technological progress as cloud providers compete to differentiate their offerings through specialized services, improved security features, and advanced AI capabilities.
AWS Continues to Reign in the Cloud Market Amid Growing Rivalry
Amazon Web Services (AWS) still holds the crown in the cloud computing industry in 2025, securing 30% of the worldwide market share in the second quarter. This is a minor increase from 29% in Q1 2025, but a 2% drop from the same time last year. Despite the intensifying competition, the cloud titan based in Seattle has managed to keep a remarkably consistent position, with market share varying between 29% and 33% over the past few years.
In Q2 2025, AWS pulled in a whopping $30.9 billion in total sales, marking a remarkable 17% growth from the previous year. This performance shows that AWS continues to successfully expand its operations and meet the needs of enterprises across a broad range of customers. The company’s wide array of services, global infrastructure, and established relationships with enterprises are competitive advantages that competitors find hard to equal in terms of breadth and depth.
The Big Three Cloud Providers Dominate with 63% of Market Share
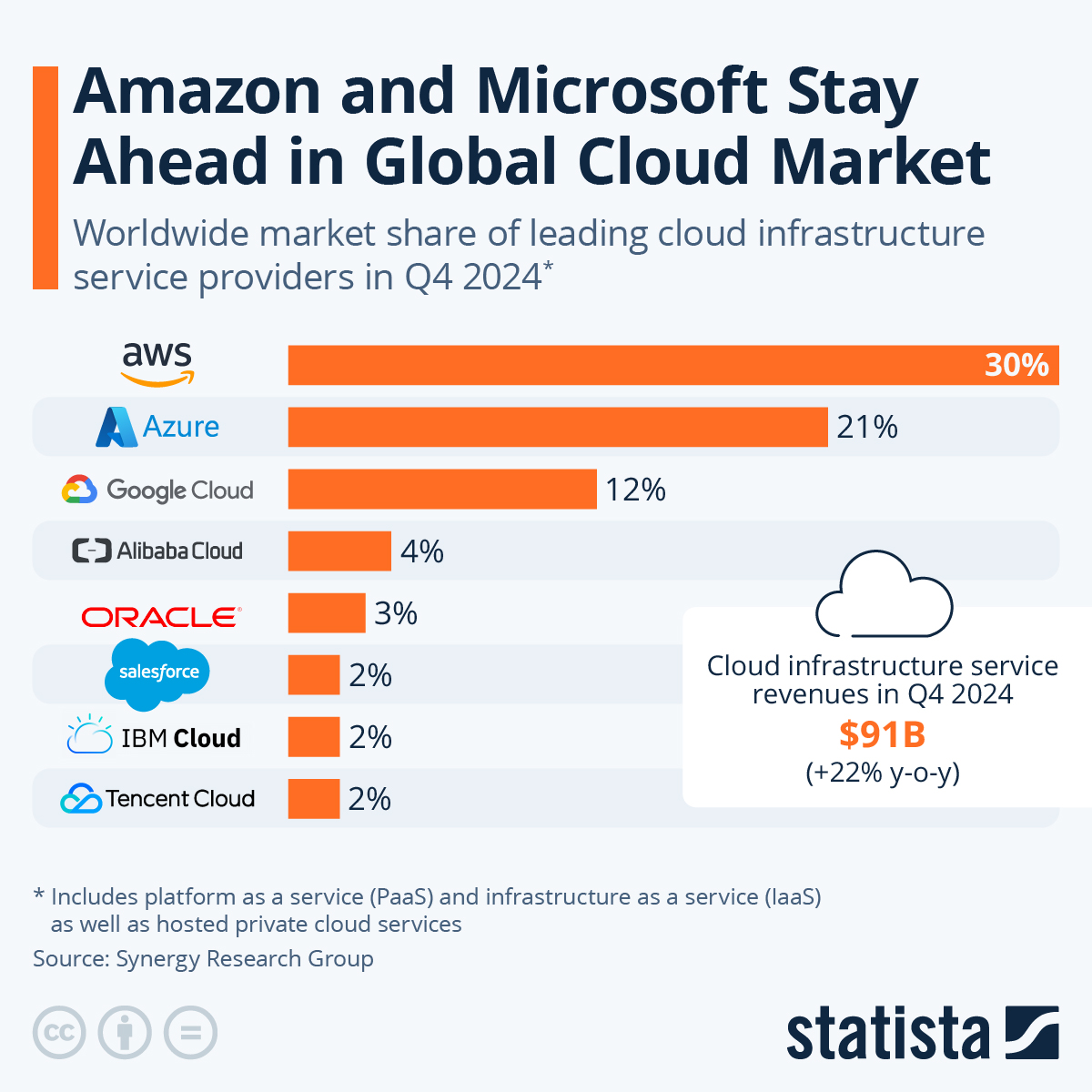
According to Synergy Research Group, Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud—often referred to as the “Big Three”—held 63% of the global enterprise cloud infrastructure services market in Q2 2025. This significant market share underscores the considerable barriers to entry for newcomers and the benefits of scale in the cloud infrastructure industry.
Even though the Big Three continue to be the leaders, the competition among them is fiercer than ever. Every provider is putting a lot of money into expanding their infrastructure, innovating their services, and creating solutions for specific industries to get a piece of the increasing cloud spending in all sectors. The other 37% of the market is divided among many smaller providers, with many focusing on local markets or offerings for specific industries to create defensible niches.
 You will find more infographics at Statista
You will find more infographics at Statista
AWS Tops the Charts with 30% Market Share
In 2025, AWS is still the undisputed leader in the market with a 30% share, significantly ahead of its closest rival. The company’s status as a pioneer continues to provide advantages, as it offers the most extensive and in-depth range of services in the sector. AWS currently provides over 200 fully-featured services, including computing, storage, databases, networking, analytics, machine learning, IoT, security, and enterprise applications.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is seeing an uptick in growth due to its artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning offerings. This surge in growth is due to the rise of generative AI. AWS has made strategic investments in custom silicon through its Graviton processors and specialized AI chips. This has helped AWS optimize the price-performance ratio for its customers while maintaining healthy margins. The growth of AWS is also being driven by enterprise migrations of mission-critical workloads. Companies are moving beyond initial cloud experimentation and are now focusing on comprehensive digital transformation.
- Market share of 30% in the second quarter of 2025 (an increase from 29% in the first quarter of 2025)
- Quarterly revenue of $30.9 billion (an increase of 17% year-over-year)
- Leading the market in 6 out of 7 global regions
- More than 200 cloud services across 26 geographic regions
- Strongest position in retail, media, and technology sectors
Microsoft Azure Retains 20% Despite Recent Decline
Microsoft Azure held 20% of the global cloud market in the second quarter of 2025, a worrying 3-point drop from the same period last year when it had a 23% market share. This drop is particularly significant given the company’s aggressive investments in AI capabilities and enterprise solutions. Azure’s position has been impacted by increased competition from both AWS and Google Cloud, as well as difficulties in maintaining growth rates as its revenue base grows.
Even though Azure’s market share has decreased, it continues to use Microsoft’s strong enterprise relationships and integrated software ecosystem to its advantage. The seamless integration with Microsoft 365, Dynamics, and other productivity tools makes a strong case for organizations that are already invested in the Microsoft ecosystem. The company’s AI capabilities, especially through its partnership with OpenAI, is a major factor contributing to growth as enterprises look to implement generative AI solutions across their operations.
Google Cloud Hits New High with 13% Market Share
Google Cloud has reached a new milestone with a 13% worldwide market share in Q2 2025, a 1% increase from Q1 2025 and Q2 2024. This growth rate makes Google Cloud the fastest growing major provider in terms of percentage, largely due to its focus on AI and data analytics. The consistent increase in market share shows that Google Cloud’s strategy to stand out with AI, analytics, and developer-friendly tools is appealing to businesses.
Google Cloud’s rapid growth is primarily due to its dominance in AI infrastructure and tools, which have drawn in organizations wanting to use advanced machine learning and generative AI capabilities. The provider’s industry-specific solutions for sectors such as healthcare, financial services, and retail have also added to its growth, as it expands beyond its traditional stronghold in the tech sector. Google Cloud’s open approach and robust hybrid cloud capabilities via Anthos have also bolstered its standing among businesses implementing multi-cloud strategies.
2025 Sees Unprecedented Growth in the Market
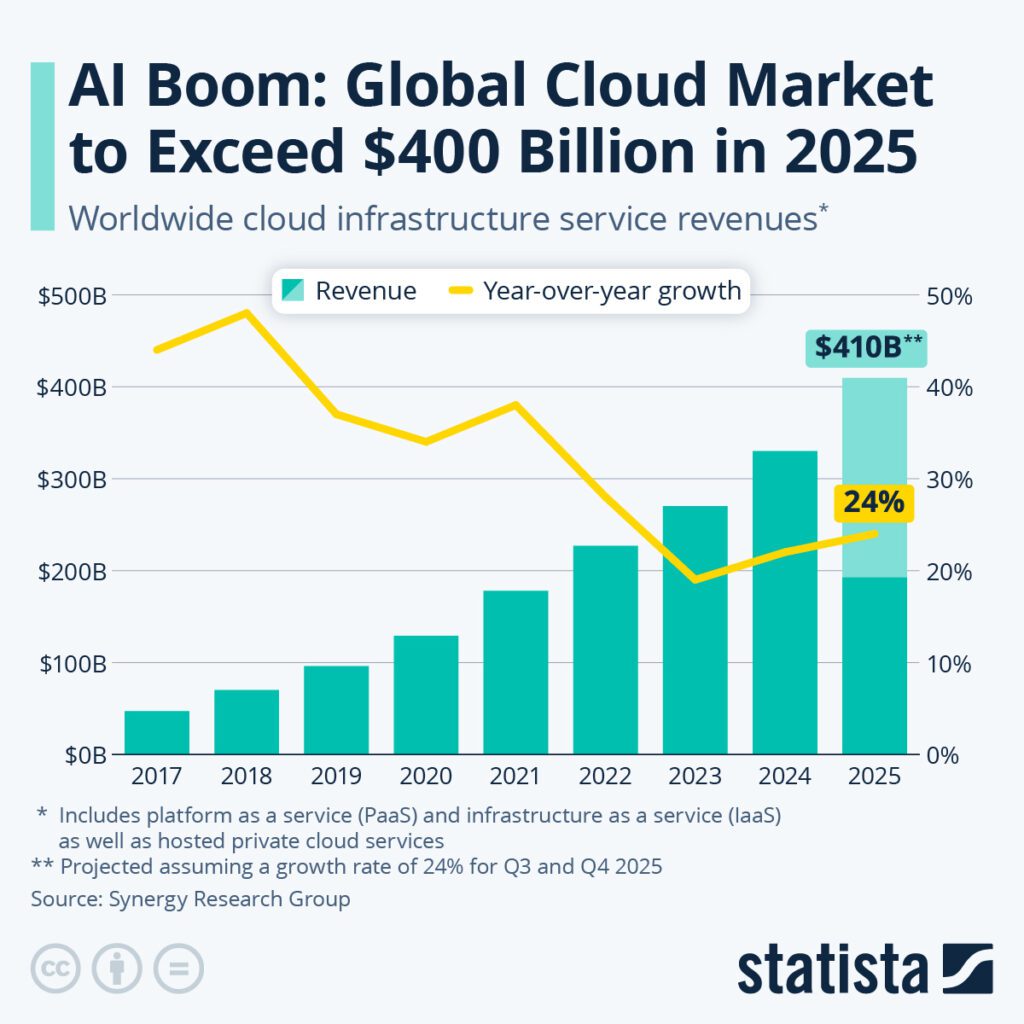
In 2025, the global cloud infrastructure market continues to grow impressively, with spending reaching levels never seen before. The total spending on cloud services reached $99 billion in just the second quarter, putting the industry on track to exceed $400 billion in a single calendar year for the first time. This impressive growth is happening despite economic challenges in some regions, showing just how essential cloud infrastructure has become to the operation of modern businesses.
“Cloud IT infrastructure spending …” from www.statista.com and used with no modifications.
Companies around the world are adopting cloud technology at a rapid pace, especially in the Asia-Pacific region where digital transformation projects are booming. The ongoing transition from legacy systems, the growth of digital business models, and the rising demand for AI capabilities are all fueling this market growth. Importantly, spending on cloud technology is increasingly viewed as a strategic investment, not just an IT cost.
Competition has escalated among the three major cloud providers, who are rapidly growing their global footprints by adding new data center regions and availability zones. This infrastructure growth is partly driven by data sovereignty needs, but it also reflects the increasing demand for low-latency access to cloud services in various geographic locations. In response, regional providers are highlighting their local expertise, regulatory compliance capabilities, and specialized industry knowledge.
Here are some key points to remember:
- Market growth rate for the year-over-year was 25% in Q2 2025
- The total spending across all cloud segments for the quarter was $99 billion
- Generative AI cloud services saw growth rates of 140-180%
- 50% of the market growth was directly due to AI-related workloads
- Enterprise multi-cloud adoption increased by 37% compared to 2024
Global Spending Reached $99 Billion in Q2 2025
In the second quarter of 2025, the cloud services market hit an impressive $99 billion. This was a 25% increase from the same quarter in the previous year. The growth rate for this quarter actually showed a re-acceleration of market growth compared to 2023-2024. This was largely due to the boom in AI and the high computing requirements it demands. Industry analysts predict that the total cloud spending for 2025 will easily exceed $400 billion. This will be a significant landmark for the industry.
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) saw a year-over-year growth of 27%
- Platform as a Service (PaaS) was the fastest-growing segment, with a growth of 29%
- Software as a Service (SaaS) continued to grow steadily at 22%
- AI-specific cloud services saw an explosive growth of 140-180%
- Private and hybrid cloud implementations saw an increase of 21%
There has also been an evolution in the composition of cloud spending. Platform as a Service offerings are seeing particularly strong adoption as organizations look to streamline the development and deployment of applications. The growth of PaaS has been outpacing other segments in percentage terms, due to the contributions from container orchestration platforms, serverless computing frameworks, and AI development environments. This shift is indicative of a maturing market, where customers are moving up the stack from basic infrastructure to higher-value cloud services.
It’s worth mentioning that spending on cloud services is now spread out across a variety of industries. Industries like financial services, healthcare, manufacturing, and the public sector, which have typically been more hesitant to adopt cloud services, are now some of the fastest growing customer segments. This expansion of the customer base gives cloud providers more stability and opens up new opportunities for solutions and services that are specific to each industry.
Speeding Up Digital Transformation for Businesses
In 2025, businesses have rapidly advanced their digital transformation goals, and cloud infrastructure has been at the core of these advancements. Companies are gradually moving away from the “lift and shift” methods and are adopting cloud-native architectures and practices that provide more flexibility for their businesses. The shift to remote and hybrid work models due to the pandemic has changed the priorities of IT, making cloud-based collaboration and productivity tools a necessity rather than a luxury.
The need to modernize outdated applications is one of the main reasons businesses are moving to the cloud. They see the difficulties of keeping old systems in-house and are looking for better solutions. Cloud providers are making it easier for businesses to make the switch by offering better migration tools, evaluation methods, and managed services. This is especially true in industries that have a lot of technical debt, like banking, insurance, and government.
Developing Applications for the Cloud
As of 2025, the standard way of creating new software is to build it for the cloud from the start. This approach has led to a surge in the use of container services, microservices architectures, and serverless computing platforms. Instead of just moving old workloads to the cloud, companies are now designing applications specifically to make the most of what the cloud has to offer. This change has made it possible to innovate more quickly, scale more effectively, and use resources more efficiently.
Kubernetes has become the go-to standard for container orchestration, and managed Kubernetes services offered by major cloud providers are being adopted at an impressive rate. The complexity of managing Kubernetes environments has pushed many organizations to opt for managed services instead of self-hosted deployments, which has led to the growth of PaaS offerings. Serverless computing is increasingly popular for event-driven workloads and microservices, as it allows developers to focus on coding rather than managing infrastructure.
Embracing Multi-Cloud Strategies
In 2025, multi-cloud strategies have become the norm, with 72% of businesses now using services from at least two major cloud providers, according to recent industry surveys. This trend is driven by a desire to prevent vendor lock-in, take advantage of the best capabilities on the market, improve disaster recovery stances, and meet diverse geographic and compliance requirements. The complexity of managing multi-cloud environments has led to a high demand for unified management tools, cloud-agnostic frameworks, and professional services to help navigate the challenges of operating across different platforms.
Trends in Cloud Adoption Across Different Industries
In 2025, the trend in cloud adoption is becoming more and more industry-specific, with solutions being customized to meet the unique needs of different sectors. Cloud offerings that are focused on a specific vertical and combine infrastructure, platforms, and software with functionality that is specific to that domain are becoming more popular. These industry-specific clouds address regulatory compliance, unique workflow requirements, and integration with specialized systems that general-purpose solutions often struggle to accommodate.
The concept of the “industry cloud” is a sign of the market’s maturation, transitioning from basic infrastructure to business solutions that tackle specific sector issues head-on. In response, leading cloud providers have started to form dedicated industry teams, acquire specialized software vendors, and construct partner ecosystems that focus on vertical solutions. This shift is leading to new competitive dynamics where industry knowledge is just as crucial as technological capabilities when it comes to securing enterprise cloud business.
Financial Services Cloud Adoption Trends
In 2025, the financial sector has seen a significant uptick in cloud adoption, with even the most traditionally risk-averse banks beginning to utilize cloud infrastructure for their most important workloads. The financial sector’s cloud migration trends are typified by a strong focus on security, regulatory compliance, and data governance, with hybrid architectures still being the norm for core banking functions. Cloud providers have reacted by offering specialized financial services products that tackle these issues while also providing the flexibility required to compete with fintech challengers.
Solutions for Healthcare Compliance
In 2025, healthcare organizations have adopted cloud infrastructure at never before seen rates. This is due to the need for scalable solutions to handle the explosive growth in healthcare data volumes. Traditional on-site infrastructure is having difficulty accommodating the petabytes of information being generated by electronic health records, medical imaging, genomic data, and connected medical devices. To meet HIPAA, GDPR, and other regulatory requirements, cloud providers have created specialized healthcare offerings with improved security and compliance capabilities.
COVID-19 has forever changed the landscape of healthcare technology, pushing telehealth to the forefront and increasing the need for cloud-based clinical collaboration tools. Healthcare providers have come to see cloud infrastructure as a necessity for providing virtual care, managing population health, and advanced analytics. AI-powered healthcare applications, especially in diagnostic imaging and clinical decision support, are driving the adoption of high-performance cloud computing resources.
Efforts to make patient data more interoperable have also played a role in the healthcare industry’s adoption of cloud technology, with health information exchanges based in the cloud becoming more popular. The need to share patient information securely across different care settings, while also ensuring privacy and compliance, has led to increased demand for specialized cloud solutions. This trend is likely to speed up as more regulatory mandates related to the interoperability of healthcare data come into effect.
- 73% of healthcare organizations now host clinical applications in the cloud
- Medical imaging storage in the cloud grew 87% year-over-year
- Healthcare-specific cloud offerings from major providers grew 62%
- Telehealth platforms remain 85% cloud-based in 2025
- HIPAA-compliant cloud services expanded offerings by 41%
Retail and E-commerce Cloud Adoption
Retail and e-commerce companies have dramatically expanded their cloud infrastructure investments in 2025 to support omnichannel customer experiences and handle increasingly dynamic demand patterns. Cloud-based commerce platforms that integrate online and offline channels have become essential as consumers expect seamless shopping experiences across touchpoints. The ability to rapidly scale during peak shopping periods while maintaining cost efficiency during quieter times remains a key driver for cloud adoption in this sector.
More and more retailers are turning to cloud-based analytics and AI features to better understand their customers, manage inventory more effectively, and customize shopping experiences. Merging brick-and-mortar stores with online platforms requires real-time data processing and analysis, a service that only cloud infrastructure can provide. Supply chain visibility has become especially important, and cloud-based platforms allow retailers to monitor and manage intricate global supply networks with increased flexibility.
Adoption of Digital Twins and IoT Integration in Manufacturing
Manufacturing companies have adopted cloud infrastructure to aid in the implementation of digital twins and Industrial IoT (IIoT) initiatives that are revolutionizing production environments. Digital twins, which are virtual models of physical assets, processes, and systems, need significant computing resources for simulation and real-time analysis, thus increasing the demand for scalable cloud infrastructure. In response, cloud providers have offered specialized manufacturing solutions that merge IoT connectivity, edge computing capabilities, and advanced analytics specifically created for industrial applications.
In manufacturing, the fusion of operational technology (OT) and information technology (IT) has become more rapid. Cloud platforms are increasingly acting as the integration layer between these traditionally separate domains. Smart factories that use cloud-connected equipment, predictive maintenance systems, and automated quality control processes are becoming the norm rather than groundbreaking experiments. This trend is opening up significant opportunities for cloud providers that can effectively bridge the gap between OT and IT with strong security models and specialized industrial solutions.
Security and Compliance Needs
The adoption of the enterprise cloud in 2025 is still largely driven by the changing needs for security and compliance. The growing regulatory environment across regions has created complex needs that differ by industry and location, prompting cloud providers to create increasingly advanced compliance frameworks. Companies are now assessing cloud providers not only based on technical abilities but also on their capacity to meet specific regulatory standards such as GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, and emerging AI governance regulations.
Cloud security has grown up a lot, and now, zero trust architectures are seen as standard practice, not just something new and exciting. People understand the shared responsibility model better, and businesses are taking a more active role in making sure they’re secure in the cloud. Sovereign cloud offerings, which keep data in one place and meet strict national security requirements, have really taken off in 2025. This is especially true in Europe, Asia, and the Middle East.
Importance of Performance and Latency
In 2025, performance needs still dictate choices for cloud deployment, with applications sensitive to latency prompting providers to grow their edge computing abilities. The spread of 5G networks has opened up new opportunities for distributed cloud designs that put computing resources nearer to end users and connected devices. This trend is especially noticeable in applications such as self-driving cars, augmented reality, and industrial IoT, where latency of even a few milliseconds can have major impacts.
Cloud providers have reacted by dramatically increasing their global points of presence, with the largest providers now boasting thousands of edge locations. As providers create seamless platforms that automatically optimize workload placement based on performance requirements, the line between centralized cloud and edge infrastructure is increasingly blurring. This development allows organizations to deploy applications across a continuum from central cloud regions to edge locations without managing completely separate environments.
Cloud providers are concentrating on improving database performance, offering services that are more specialized and optimized for different workloads. The ability to scale database resources dynamically and consistently has become a significant differentiating factor. In-memory database options, specialized analytics databases, and multi-model databases that support different data types within a single system have all seen substantial growth in adoption.
As cloud providers expand their infrastructure at varying speeds, the performance differences between them in different regions have become more noticeable. Companies operating globally are increasingly choosing different providers for different regions based on how well they perform locally, instead of sticking with one provider worldwide. This has helped multi-cloud strategies, which take advantage of regional performance differences, to grow.
Performance Benchmarking for Cloud: Results from 2025
After conducting worldwide tests across 50 regions and 500 service combinations, we have observed significant trends in the cloud infrastructure service providers market.
- AWS performs the best in North America (average compute speed 18% faster)
- Azure is the top performer in Europe (37% better throughput in storage)
- Google Cloud has the most consistent performance worldwide (12% less variance)
- Alibaba is the best performer in the Asia-Pacific region (29% less latency)
- Oracle is the leader in database performance (transaction processing is 44% faster)
Data Source: CloudBench Global Performance Index, Q2 2025
Avoiding Vendor Lock-in
Worries about vendor lock-in continue to play a crucial role in shaping cloud strategy decisions. Businesses are giving more importance to architectural strategies that maintain flexibility. Deployments based on containers using Kubernetes have become the favored method for ensuring workload portability across different environments. The increasing use of infrastructure-as-code tools that can target more than one cloud platform shows that organizations want to prevent over-reliance on any one provider’s proprietary services.
Despite these efforts, the reality of cloud migration in 2025 reveals that workload portability often remains challenging in practice. As organizations adopt more advanced platform services and specialized capabilities, the technical debt associated with provider-specific implementations continues to accumulate. This tension between leveraging provider-specific advantages and maintaining portability represents one of the core strategic challenges facing enterprise IT leaders today. Many organizations are addressing this through deliberate strategies that classify workloads by portability requirements, with some designated for provider-specific implementations and others maintained in more portable configurations.
Looking Ahead: The Rest of 2025 and Beyond
As we look to the remainder of 2025 and the years to come, the cloud infrastructure market is set to undergo significant changes. These changes will be shaped by a number of key trends, including the continued influence of artificial intelligence, regulatory changes, sustainability efforts, and changes in the competitive landscape among providers. Organizations that can anticipate these changes will be better equipped to use cloud technologies as a competitive advantage, rather than just as a method of IT delivery.
Anticipated Annual Growth of Over 20% Until 2030
Despite the already considerable size of the cloud infrastructure market, analysts predict continued growth at rates exceeding 20% annually until 2030. This persistent expansion reflects both the deepening adoption of the cloud within existing customer organizations and the ongoing migration of new sectors and regions to cloud-based models. Total cloud spending is expected to exceed $1 trillion annually by 2028, representing one of the largest and most significant technology markets in history. This growth path will be supported by increasing diversification of cloud services beyond the traditional IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS categories to include specialized offerings targeting specific industry needs, technical requirements, and emerging use cases.
AI-Driven Growth Continues
Artificial intelligence is expected to continue to be the biggest factor in the growth of cloud infrastructure for the rest of the decade. As AI models become more complex, the computational needs for training and deploying these models are growing at an exponential rate. This is creating an unprecedented need for specialized cloud resources. In response, cloud providers are investing heavily in infrastructure that is optimized for AI, including custom silicon, high-bandwidth interconnects, and memory architectures that are designed specifically for machine learning workloads. At the same time, AI capabilities are being integrated into virtually every aspect of cloud services. This is making these platforms more accessible, intelligent, and valuable to customers in all sectors. This creates a cycle of adoption and innovation that will sustain market growth.
Regional Market Trends
Regional differences in cloud adoption and growth will become more evident as we move towards 2025, reflecting disparities in digital readiness, regulatory climates, and economic situations. The Asia-Pacific region is expected to see the highest growth rates, with markets in India and Southeast Asia seeing especially quick adoption as digital transformation efforts pick up speed. Latin America is also showing promise as a high-growth region, although infrastructure constraints in some areas still pose obstacles to cloud deployment.
Local cloud providers are becoming more powerful in markets where data sovereignty and local regulations give domestic operators an edge. This trend is especially noticeable in China, where local providers rule the market, but it’s also becoming more common in Europe, the Middle East, and parts of Asia where regulatory requirements and government procurement policies are increasingly leaning towards local or regional providers. The big global cloud providers are reacting by forming more partnerships with local operators and creating sovereign cloud services that meet regional needs while maintaining access to their global technology stacks.
Regulation and Cloud Providers
Regulations for cloud services are rapidly changing and have significant implications for providers and customers. Data privacy rules, AI governance frameworks, antitrust issues, and critical infrastructure mandates are all influencing how cloud services can be delivered and used in different markets. Cloud providers are heavily investing in compliance capabilities and government relations to navigate this increasingly complex environment. The ability to adapt to regulations while maintaining global scale and service consistency will be a key differentiator for successful cloud providers throughout the rest of the decade, especially as more industries with strict regulations speed up their cloud adoption.
Common Questions
As companies grapple with their cloud infrastructure choices in 2025, there are a few recurring questions about the current market situation and strategic considerations. Understanding these key features of the cloud environment can help decision makers create better strategies for cloud adoption, migration, and optimization. The questions below are the ones we hear most often from corporate clients evaluating their cloud strategies.
The insights provided here are grounded in extensive market research, thousands of customer interactions, and thorough performance benchmarking across leading cloud platforms throughout 2024 and the early part of 2025. While specific organizational needs may differ, these insights offer a solid foundation for grasping the present state of cloud infrastructure and probable future trends.
Who is the top cloud provider in 2025?
As of 2025, AWS still holds the title of the largest cloud infrastructure provider, boasting a 30% market share. They’re followed by Microsoft Azure with a 20% share, and Google Cloud with 13%. AWS has managed to hold onto its leadership role since it essentially invented the modern cloud infrastructure market, although its once-dominant market share has slowly decreased from highs over 33% as competition has grown. Despite recent gains by Microsoft and Google, AWS’s wide-ranging service portfolio, global infrastructure presence, and first-mover advantage have allowed it to maintain its status as the market leader in most regions and industry verticals.
What’s the growth rate of the cloud market since 2024?
From 2024 to 2025, the worldwide cloud infrastructure market has seen a roughly 25% annual growth rate, hitting $99 billion in Q2 2025 quarterly spending. This is a faster growth rate than what we saw from 2023-2024, and it’s mainly due to workloads related to artificial intelligence and ongoing digital transformation efforts. For 2025 as a whole, the total market is projected to surpass $400 billion, which would be a significant industry milestone.
Not all cloud segments or geographies are experiencing the same rate of growth. AI-related cloud services are seeing a whopping annual growth rate of 140-180%, while traditional infrastructure services are growing at a more modest 15-20%. Similarly, emerging markets in Asia and Latin America are seeing their growth rates exceed 35%, while more mature markets like North America and Western Europe are growing at a rate of 18-22%. This variation underscores the increasingly diverse and specialized nature of the cloud infrastructure market as it continues to evolve.
What is driving Google Cloud’s market share growth in 2025?
Google Cloud has grown its market share to an all-time high of 13% in Q2 2025, thanks to several key factors. The most significant of these is Google’s leadership in AI and data analytics. Early investments in custom AI accelerators, robust machine learning platforms, and AI tools that are easy for developers to use have put Google Cloud in a strong position as more businesses adopt AI. Google Cloud has also made great strides in overcoming the obstacles that previously prevented businesses from adopting it. It has expanded its global infrastructure, built stronger partnerships, and created more comprehensive industry-specific solutions for sectors such as healthcare, financial services, and retail.
How has AI influenced spending on cloud infrastructure?
In 2025, artificial intelligence became the primary driver of growth for cloud infrastructure spending, contributing directly to approximately 50% of all market growth. The computational requirements for training and deploying increasingly complex AI models have created an unprecedented demand for specialized cloud resources, such as GPU-accelerated computing instances, high-performance storage, and low-latency networking. Beyond these direct impacts on infrastructure, AI is also indirectly driving cloud adoption by enabling new categories of applications and use cases that benefit from cloud deployment models. The integration of AI capabilities into virtually all aspects of enterprise software is further accelerating the migration to cloud platforms that offer advanced AI services and optimized infrastructure.
How are regional cloud providers standing up to the Big Three?
Regional cloud providers are creating competitive niches against the global hyperscalers by concentrating on a few key differentiators. Data sovereignty capabilities that ensure data residency within specific jurisdictions have become especially valuable as regulatory requirements become more stringent in many regions. Local providers often have stronger relationships with government agencies and regulated industries in their home markets, providing advantages in sectors sensitive to compliance. Industry-specific expertise and solutions tailored to local market requirements also create competitive opportunities for regional providers.
Regional providers are increasingly teaming up with global hyperscalers to create hybrid offerings that merge local presence with access to global technology platforms. These setups enable regional providers to concentrate on customer relationships and compliance while benefiting from the R&D capabilities and economies of scale of the major global providers. This model of cooperative competition is creating a more complex market landscape where the line between global and regional providers is becoming blurred.
Regional providers’ success is largely determined by the market, with the most solid positions being established in regions with strict data sovereignty requirements, unique regulatory frameworks, or a strong government preference for local technology providers. China is the most striking example of regional provider dominance, with Alibaba, Tencent, and other domestic providers controlling more than 80% of the local market. Similar trends are beginning to emerge, albeit less dramatically, in markets such as Europe, the Middle East, and parts of Asia-Pacific.